Топик: Science / Наука
We are living in the modern world, full of computers, automatic devices, gadgets, cell phones and many other different interesting and useful things that technological progress has given us for usage. Although not even years have passed as we couldn’t even dream about time when it would be enough just to tap on a screen and get connected with the other person on the different end of the world.
Science has given us possibility to fly into space and step on the moon, to start studying different parts of our galaxy and even farther. For example, what wonderful pictures of our galaxy and planets and stars surrounding Earth Hubble telescope has showed to us. Now we can develop further and maybe ever step on the other planets and even populate it.

Technology has considerably made our life easier due to different discoveries. For example, nowadays we can travel with extremely high speed in different directions: many countries have high-speed trains which help us to feel comfortable all the way.
Older people have different devices that have highly improved the level of their life, such as special cars for driving or hearing aid that helps them to no more feel useless in the society.
On the other hand al this computerized environment may damage us too. Our children spend more and more time playing computer games, texting their friends instead of meeting them in the streets, living more and more in their own virtual world. Girls try to compete whose cell phone or tablet is better and more modern, or who has more friends on Facebook.
Anyway technology has its advantages and disadvantages, but we cannot escape from progress, the development is inevitable. But our responsibility is to preserve ourselves as modern, just and peaceful civilization.
Мы живем в современном мире, переполненном компьютерами, автоматическими устройствами, мобильными телефонами и другими интересными и полезными, которые нам дал в пользование технический прогресс. Хотя еще двадцать лет назад мы и мечтать не могли о времени, когда будет достаточно коснуться экрана и соединиться с человеком на другом конце земли.
Наука дала нам возможность полететь в космос и ступить на луну, начать изучать разные части нашей галактики и даже дальше. Например, какие прекрасные фотографии нашей галактики, ее планет и звезд окружающих Землю подарил нам телескоп Хаббл. И сейчас мы можем развиваться и дальше, и может быть, ступим на другие планеты и даже поселимся на них.
Технологии сделали нашу жизнь значительно легче, благодаря разным открытиям. Например, сегодня мы можем путешествовать с невероятно высокими скоростями в разные направления: во многих странах уже есть высокоскоростные поезда, позволяющие нам чувствовать себя комфортно в пути.

У пожилых людей появилось множество разных устройств, которые сильно улучшили их уровень жизни, такие как специальные автомобили и слуховые аппараты, позволяющие им чувствовать себя полезными обществу.
С другой стороны вся эта компьютеризированная среда может и навредить. Наши дети проводят все больше и больше времени, играя в компьютерные игры, переписываясь с друзьями, вместо того, чтобы встретиться на улице. Они все больше и больше живут в своем виртуальном мире. Девочки стали соревноваться у кого мобильный телефон лучше и современней, или у кого больше друзей в социальной сети.
Все равно у технологий есть свои преимущества и недостатки, но мы не можем убежать от прогресса, развитие неизбежно. Но наша ответственность в том, чтобы сохранить человечество современным, справедливым и мирным.
Конспект урока английского языка в 8 классе. Мир науки и техники
Раздел 4, учебник для 8 класса школ с углублённым изучением английского языка.
Авторы УМК О.В. Афанасьева, И.В.Михеева
Урок с использованием технологии «Развитие критического мышления».
Автор: Дьякова Светлана Анатольевна, учитель МБОУ СОШ №6 с углублённым изучением английского языка г. Апатиты, Мурманской области
Цель урока: Совершенствование навыков чтения и устной речи по теме « Мир науки и техники »
Задачи урока:
Образовательные: познакомить учащихся с биографией английского изобретателя А. Белла
Развивающие: развивать навыки устной речи, аудирования и понимания прочитанного; умение работать в группе; графически оформлять текстовый материал; творчески интерпретировать имеющуюся информацию; распределять информацию по степени новизны и значимости; обобщать полученные знания.
Воспитательные: воспитывать культуру общения
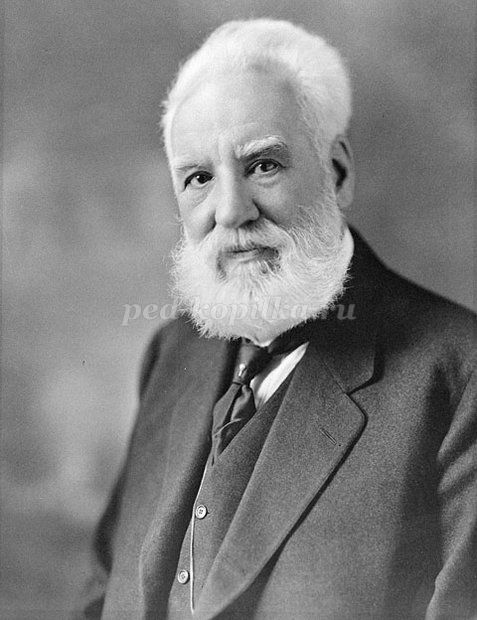
2.Учитель создает условия для определения «знаю-хочу знать» по теме для осознания целей урока.
а)Open your books p.144 ex.12. Учащиеся выполняют предтекстовое задание.
в)Учитель предлагает учащимся составить кластер. A.Bell’s invention (запись на доске)
Work in pairs. Write in your sheets of paper. «A. Bell’s invention».
Учитель задает вопрос: «Что вы знаете о данном человеке и его изобретении? Озвучивание и совместное оформление кластера.
II. Основной этап урока.
Осмыление. Методы и приемы: инсерт (чтение текста с пометками),cтратегия «Вопросительные слова»
1.Учитель предлагает прочитать текст «The man and his work» на стр. 144-145, делая на полях пометки.
Read the text «The man and his work» while reading make notes in your papers :
При чтении текста дети расставляют специальные пометки.
После чтения школьники обсуждают результаты в парах и составляют одну на двоих таблицу.
Учащиеся работают с текстом учебника.
+ соответствует тому, что знаю
— новая информация
! противоречит моим представлениям, критически к этому отношусь
? мало информации, хотелось бы узнать побольше
Коллективное обсуждение полученной информации. Выполняются упражнения по прочитанному тексту (стр. 146 упр.13,14).
2.Интеллектуальная разгрузка
-Try to read Hamlet’s monolog”To be or not to be”artistically in the A.Bell’s manner. ( at the demonstration of his machine )
William Shakespeare:
To be, or not to be: that is the question:
Whether ’tis nobler in the mind to suffer
The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune,
Or to take arms against a sea of troubles,
And by opposing end them?
To die: to sleep;No more; and by a sleep to say we end
The heart-ache and the thousand natural shocks
That flesh is heir to, ’tis a consummation
Devoutly to be wish’d. To die, to sleep;To sleep:
perchance to dream: ay, there’s the rub;
For in that sleep of death what dreams may come
When we have shuffled off this mortal coil,
Must give us pause: there’s the respect
That makes calamity of so long life;...
-Прочитайте монолог Гамлета от своего лица (на презентации первой модели телефона)
Б. Пастернак
Вильям Шекспир: монолог Гамлета
«Быть или не быть, вот в чём вопрос»
Достойно ль
Смиряться под ударами судьбы,
Иль надо оказать сопротивленье
И в смертной схватке с целым морем бед
Покончить с ними? Умереть. Забыться.
И знать, что этим обрываешь цепь
Сердечных мук и тысячи лишений,
Присущих телу. Это ли не цель
Желанная?
Скончаться.
Сном забыться.Уснуть. и видеть сны?
Вот и ответ.
Какие сны в том смертном сне приснятся,
Когда покров земного чувства снят?
Вот в чем разгадка.
Вот что удлиняет
Несчастьям нашим жизнь на столько лет.
3.Обучение устной речи.
Используется cтратегия «Вопросительные слова» (упр.12)Учитель предлагает учащимся составить в группах как можно больше вопросительных предложений. Каждой группе дан список с вопросительными словами:
-who
-what
-where
-how
-why
-which
-for whom
Примеры вопросительных предложений:
Who was born in Scotland7
Where did he spend his childhood?
What did he do after graduating from the university of London?
Why did Bell take T.Watson as his assistant?
Эту работу можно осуществлять как индивидуально, так и в парах. Далее ученики обсуждают свои списки и выбирают два наиболее интересных (продуктивных, неожиданных, проницательных и т.д.) вопроса. Теперь можно организовать целенаправленную работу с информацией – поиск ответов на свои вопросы. Причём преподаватель получает объективные данные о том, что больше всего интересует детей в данной теме.
III.Заключительный этап урока. Рефлексия
-Возвращение к кластеру.
Let`s return to our cluster and add new information to it. Учащиеся добавляют новую информацию.
3.Учитель предлагает учащимся составить синквейн.
I think now you can talk about «A. Bell’s invention».
And our task is to summarize everything we know about the invention of the telephone .
We have to make only 5 points:
1. What are we talking today about?
(1 word)-Invention
2. Give me 2 adjectives characterizing the invention .
The greatest, famous
3. Give me 3 verbs.
Stretched,vibrated,connected
4. Give a sentence , describing the event.
The telephone receiver was connected with transmitter
5.Give me only one word, a synonym of the word invention -Discovery
Учащиеся составляют синквейн, затем идет представление синквейна перед классом.
-«Бортовой журнал»(письменная рефлексия)
Complete these sentences. Use the information from the text «The Man and His Work».
Some people believe that inventions occur . .(as he need arises)
Alexander Bell and his brother became interested in . .(with the human voice)
After graduating from the University of London Alexander . .(was the teacher of the deaf)
This little machine that he called the phonautograph, gave him a key . .(to the invention of the telephone)
The telephone receiver was connected . .(with the transmitter across the room)
Bell’s invention was immediately called . .(the greatest of the time)
«I went to bed, the night before, an unknown man, . .» (and awoke to find myself famous)
Урок английского языка в 9-м классе «Science is discovery» («Наука – открытие»)
Цель урока: развитие монологической и диалогической речи учащихся с использованием мультимедийных технологий.
Образовательные: совершенствовать умения и навыки практического владения английским языком; расширить кругозор учащихся по теме; обучить навыкам работы в мультимедийной среде.
Познавательные: активизировать лексический материал по теме “Наука”; познакомить учащихся с жизнью и деятельностью английских ученых M. Faraday и I. Newton.
Воспитательные: воспитывать умения внимательно слушать и слышать своих одноклассников; формировать уважение к их мнению; повысить интерес к изучению английского языка.
Развивающие: развивать умения высказывать мнение, делать выводы; развивать коллективную деятельность.
1. Организационный момент.
Диалог с дежурным.
What day of the week is today?
What date is today?
Who is on duty today?
Who is absent? What is up with him/her?
2. Фонетическая зарядка. (На Smart Board)
3. Знакомство с целью урока. (Тема и цель урока на Smart Board)
The subject of today lesson is “Science is Discovery. The Museum of Science and Technology of Sci Trek”. As we’re studying at school specializing in mathematics and physics, we’ll turn on them.
For your information: the word “Science” comes from a Latin word “Scire” meaning “to know”.
4. Работа с лексикой (картинки, изображающие отрасли науки).
a) Look at these drawing and say what branches of Science you can match them with. (Соединяют картинку с названием науки на интерактивной доске)
(Ребята называют) biology, astronomy, mathematics, geography, history, physics, botany, chemistry.
Листая страницы на интерактивной доске, читают определения разных отраслей науки и называет саму науку, затем проверяют правильность ответа, опуская “шторку” на Smart Board.
Read the definitions of different branches of science and match them with the names of sciences:
It is the science of the stars. It deals with celestial bodies such as our earth, its moon, the sun, the other planets (astronomy).
It is the study of the way in which language works (linguistics).
It is the science of mental life which studies human and animal behavior (psychology).
It is the science of life. It deals with great diversity of life forms (biology).
It deals with the scientific observation and study of the phenomena of weather and climate (meteorology).
в) (на доске записаны слова)
From nouns denoting professions, dealing with different branches of learning, science, art. (На интерактивной доске науки, а учащиеся образуют от этих наук профессии)
With the help of which suffixes do we form nouns? (Таблица с суффиксами)
(отвечают) -ist, -er, — ian.
Thus, let’s sum up:
We touched on different subjects belonging to different sciences.
Answer my questions:
What subjects belong to natural sciences?
— (geography, botany, biology)
What subjects belong to physical sciences?
— (physics, mathematics, chemistry)
What subjects belong to social sciences?
What subjects belong to humanities?
5. Основная часть урока.
Let’s turn to the subject of our lesson. So, «Science is Discovery».
Учитель: То learn more about science I advise you to go to the Museum of Science and Technology in Atlanta. Its name is Sci Trek. (Картинка, изображающая музей, на интерактивной доске)
Imagine that we are in the USA and want to visit it, but we don’t know how to get inside the museum. Oh, look! This is Peter Watson and his assistant.
What is your name?
— (ученик 2) Andrew Nickson.
— (учитель) Meet them. They can help us.
— (ученик 1) Glad to meet you! I am Peter Watson. I am the Public Programs at Sci Trek. The museum is great. Because you can touch everything in the museum. You can experiment with the equipment in the museum to learn more about science. It has 100 exhibits. One exhibit teaches you about electricity, another about mathematics and another about thunderstorms.
The exhibits show the principles of science in everyday lives. One of exhibit halls is the Hall of Simple Machines. There are also exhibits about Bernaulli’s principle. This is the principle about relative air pressure which engineers use to design the wings of airplanes. There is also a Hall of Electricity and Magnetism, a Hall of Light, Color and Perception. In addition to these exhibit halls there is the «Mathematics» exhibit area which is all about the different areas of mathematics.
They have performances and demonstrations about electricity and Newton’s Laws of Motion.
— (ученик 3) Are there any other exhibits? I am interested in exhibits telling about outstanding people.
— (ученик 1) Yes, there are some. One of them is about Michal Faraday. My assistant will tell you about it.
— (ученик 2) M. Faraday was born in London in a poor family. He did not learn much and spent a lot of time playing in the streets. When he was 14 he got some work in a bookseller’s shop. There he read as many books as he could. Later he became an assistant in a laboratory of one of the great scientists. Soon he become interested in electricity and at last he saw that electricity could be made by a machine. This was the beginning of all great machines that make our electricity today. Without them we can have no telephones, no radio, no television. Each of these things is invention made for man by the work of Faraday and others with electricity. (На интерактивной доске портрет M. Faraday)
Диалог между Peter Watson и учеником:
— How interesting! It’s worth visiting. Could you help us, please?
— And what about tickets? How much are they?
— For you, it is free of charge. But there are some conditions. You are:
1) to read English texts
2) solve problems
3) find out the password.
— (учитель) Our task is not an easy one.
Let’s try. If we do it successfully, we’ll get into the Museum.
To solve problems, we should memorize 4 rules of arithmetic. Do you remember them?
— (ученики): The are: addition + division:
Subtraction — multiplication x
— (учитель) I’ll give you problems to solve. Do it and say what kind of problem it is and how you solved it.
(Задачи даны на интерактивной доске, листая страницы, решают и записывают решения на интерактивной доске, а затем проверяют ответы, отодвигая “шторку” на Smart Board)
25 9 th — form boys, 18 10 th — form boys and 12 11 th — form boys belong to the
How many boys are there in the club?
Pete has 280 stamps. Alec has 273 stamps.
How many more stamps has Pete than Alec?
Mike bought 54 photos.
If he can put 6 of them on each page of his album, how many pages will he need?
There is place for 6 stamps on each page of Nick’s stamp book.
How many stamps must he have to use 8 pages?
6. Подготовка к аудированию и аудирование.
Step by step we come nearer to the museum.
Our task is to find out the password.
Only then we’ll be able to get inside the museum.
(На интерактивной доске незнакомые слова) Учитель произносит их, учащиеся повторяют.
the law of gravitation — закон тяготения
calculus [‘kжlkjul?s] — исчисление
differential calculus — дифференциальные исчисления
integral calculus — интегральные исчисления
ray [rei] — луч.
Прослушать текст 1 раз и сказать о ком он?
Listen to it once and say who this text is about?
Текст для аудирования.
The great English scientist was born not far from the university town of Cambridge in 1642. In his early years he made various things such as a clock that worked by water, a sun – dial and others.
When he grew older, he took a considerable interests in mathematics. His ability as mathematician and physicist was very important. His first experiment was carried out when he was 16 years old. In 1661 he entered the University of Cambridge where he studied mathematics.
He became famous for his contribution to mathematics by the time he was 21.
At the age of 22 he began studying the theory of gravitation.
Once he saw an apple fall from a tree and concluded that it was being attracted by a force.
At Cambridge he read the writings of Galileo and worked out the methods of calculus.
He performed many experiments with light and found that white light was made up of rays of different colors and developed differential and integral calculus. He died in 1727 at the age of 85. He was buried with honors as a national hero in Westminster Abbey.
Перед вторым прослушиванием прочитать вопросы на Smart Board.
Was Isaak Newton a bright child?
When was his first experiment carried out?
When did he begin to study the theory of gravitation?
What methods did Newton work out?
What did he find about white light?
He developed differential and integral calculus, didn’t he?
После прослушивания отвечают на вопросы и проверяют ответы, опуская “шторку” на Smart Board.
— (учитель) Now we know the password and that’s Isaak Newton (на интерактивной доске портрет Isaak Newton). Go and experiment with the equipment inside the museum.
Прошло 2 часа. Two hours later.
— (учитель) So. You spent 2 hours in the museum and learned a lot about science.
В музее ученики встретили русского мальчика Сашу. Он беседует с американским другом.
На карточках диалог между Сашей и Джоем (читают).
Источники: http://online-teacher.ru/blog/tema-science, http://ped-kopilka.ru/blogs/svetlana-anatolevna-djakova/konspekt-uroka-angliiskogo-jazyka-v-8-klase-na-temu-mir-nauki-i-tehniki.html, http://xn--i1abbnckbmcl9fb.xn--p1ai/статьи/563038/




